Human Milk and Lactation
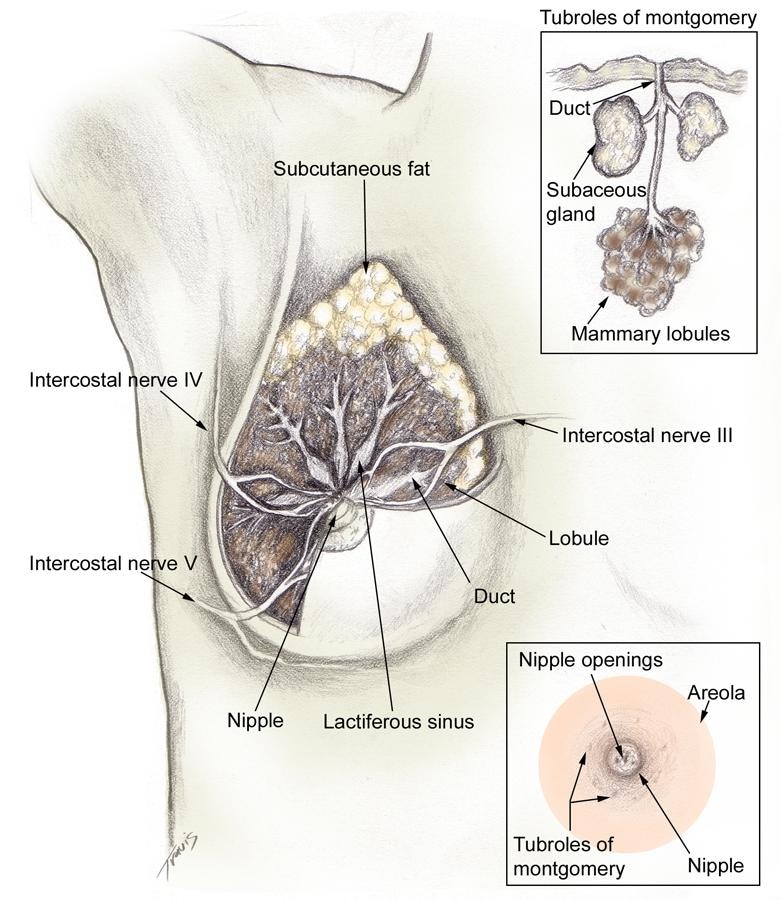
BackgroundBreast milk is thought to be the best form of nutrition for neonates and infants. The properties of human milk facilitate the transition of life from in utero to ex utero. This dynamic fluid provides a diverse array of bioactive substances to the developing infant during critical periods of brain, immune, and gut development. The clinician must be familiar with how the mammary gland produces human milk and how its properties nourish and protect the breastfeeding infant. Clinicians play a crucial role in a mother's decision to breastfeed and can facilitate her success in lactation. Although a mother may not be aware of the evidence indicating that breast milk contributes to her baby's short-term and long-term well-being, she has developed certain attitudes and cultural beliefs about breastfeeding. The issue of bonding between mother and newborn may be a strong factor; however, stronger cultural or societal barriers may result in the decision to formula feed. Such issues must be understood for successful counseling. The mother makes her decision regarding breastfeeding prior to delivery in more than 90% of cases; therefore, her choice of infant nutrition should be discussed starting in the second trimester and continue as part of an ongoing dialogue during each obstetric visit. This article reviews the development of the mammary gland (mammogenesis), the process through which the mammary gland develops the capacity to secrete milk (lactogenesis), the process of milk production (lactation), and the specific properties of human milk that make it unique and appropriate for human infants. In a related article titled Counseling the Breastfeeding Mother, the mechanics of breastfeeding and evaluation of the breastfeeding mother-infant dyad are discussed. Such articles are intended to be overviews. For a more in-depth treatise, please refer to textbooks by Lawrence and Lawrence (2005)[1] and the American Academy of Pediatrics (2006).[2] Guidelines for breastfeeding and the use of human milk have been established by the American Academy of Pediatrics.[3] PathophysiologyMammogenesisThe breast begins to develop in utero, undergoing the first of many developmental changes necessary for proper breastfeeding to occur. A bulb-shaped mammary bud can be discerned in the fetus at 18-19 weeks' gestation. Inside the bud, a rudimentary mammary ductal system is formed, which is present at birth. After birth, growth of the gland parallels that of the child until puberty. The normal anatomy of the mammary gland following pubertal development is shown in the images below.[4]
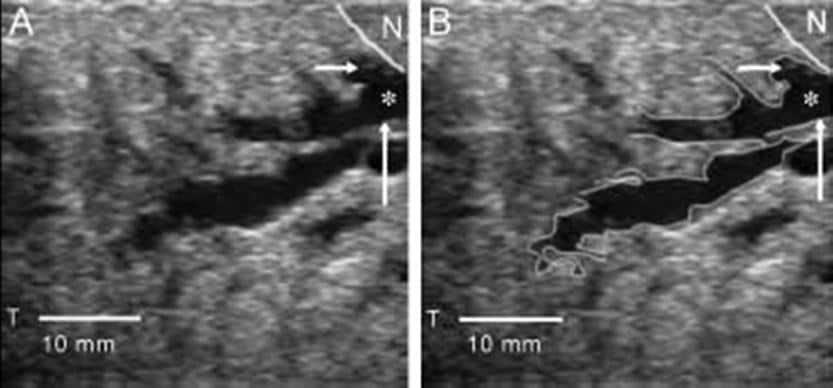
Frontal view of lactating breast. The basic unit of the mammary gland is the alveolus or acinus cell that connects to a ductule. Each ductule was believed to independently drain to a duct that, in turn, emptied into lactiferous sinuses. These lactiferous sinuses drain to 15-25 openings in the nipple, allowing milk to flow to the recipient infant. More recently, researchers such as Ramsay et al (2005) have questioned the existence of lactiferous sinuses.[5] Extensive real-time ultrasonography of 21 fully lactating women provided better understanding of the anatomy of the lactating human breast, as shown below.
(A) Ultrasound image of milk duct in the lactating breast. The duct appears as a branching hypoechoic structure within echogenic glandular tissue. (B) The ducts focused on the nipple (N) to the periphery of the breast. The walls are echogenic (up arrow) and the lumen hypoechoic (asterisk). The first branch of this duct (-->) is imaged almost directly under the nipple. On ultrasonography, milk ducts appear as superficial, hypoechoic tubular structures with echogenic walls whose milk-fat globules appear as echoes. The ducts are easily compressed, do not display typical sinuses, and anatomically appear to transport the milk rather than store it. The ducts can be traced from the base of the nipple back into the parenchyma. The mean number of main ducts greater than 0.55 mm diameter at the base of the nipple was approximately 10 for the left breast and 9 for the right breast. Although the duct diameter was increased at multiple branch points, the typical saclike appearance of lactiferous sinuses under the areola was not observed during scanning. The mean number of ducts and the diameter of the main ducts were not related to nipple diameter, areola radius, or milk production for individual breasts. Adipose and glandular tissue distribution differed widely among women but not between breasts. In addition, the proportion of glandular and fat tissue and the number and size of ducts were not related to milk production. At puberty, released estrogen stimulates breast tissue to enlarge through growth of mammary ducts into the preexisting mammary fat pad. Progesterone, secreted in the second half of the menstrual cycle, causes limited lobuloalveolar development. The effects of estrogen and progesterone facilitate the formation of the characteristic structure of the adult breast, which is the terminal duct lobular unit. However, full alveolar development and maturation of epithelium requires the hormones of pregnancy. LactogenesisIn lactogenesis, the mammary gland develops the capacity to secrete milk. Lactogenesis includes all processes necessary to transform the mammary gland from its undifferentiated state in early pregnancy to its fully differentiated state sometime after pregnancy. This fully differentiated state allows full lactation. The 2 stages of lactogenesis are discussed below. Stage 1 occurs by mid pregnancy. In stage 1, the mammary gland becomes competent to secrete milk. Lactose, total protein, and immunoglobulin concentrations increase within the secreted glandular fluid, whereas sodium and chloride concentrations decrease. The gland is now sufficiently differentiated to secrete milk, as evidenced by the fact that women often describe drops of colostrum on their nipples in the second or third trimester. However, high circulating levels of progesterone and estrogen hold the secretion of milk in check. Stage 2 of lactogenesis occurs around the time of delivery. It is defined as the onset of copious milk secretion. In stage 2, blood flow, oxygen, and glucose uptake increase, and citrate concentration increases sharply. Increased milk citrate is considered a reliable marker for the second stage of lactogenesis. Progesterone plays a key role in this stage. Removal of the placenta (ie, the source of progesterone during pregnancy) is necessary for the initiation of milk secretion; however, the placenta does not inhibit established lactation. Work by Haslam and Shyamala reveals that progesterone receptors are lost in lactating mammary tissues, thus decreasing the inhibitory effect of circulating progesterone.[6, 7] In addition, maternal secretion of insulin, growth hormone (GH), cortisol, and parathyroid hormone (PTH) facilitates the mobilization of nutrients and minerals that are required for lactation. The stages of lactation can be summarized as follows (adapted from Riordan and Auerbach, 1998):[8]
LactationSee the list below:
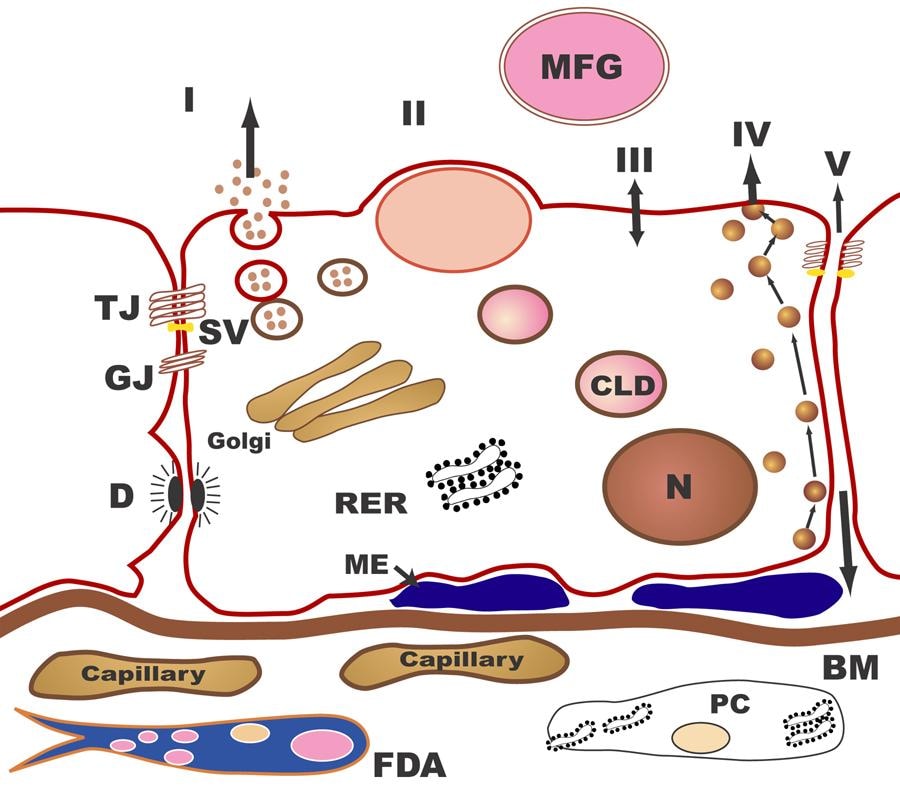
Biochemistry of human milkHuman milk is a unique, species-specific, complex nutritive fluid with immunologic and growth-promoting properties. This unique fluid actually evolves to meet the changing needs of the baby during growth and maturation. Milk synthesis and secretion by the mammary gland involve numerous cellular pathways and processes (summarized in the table below).
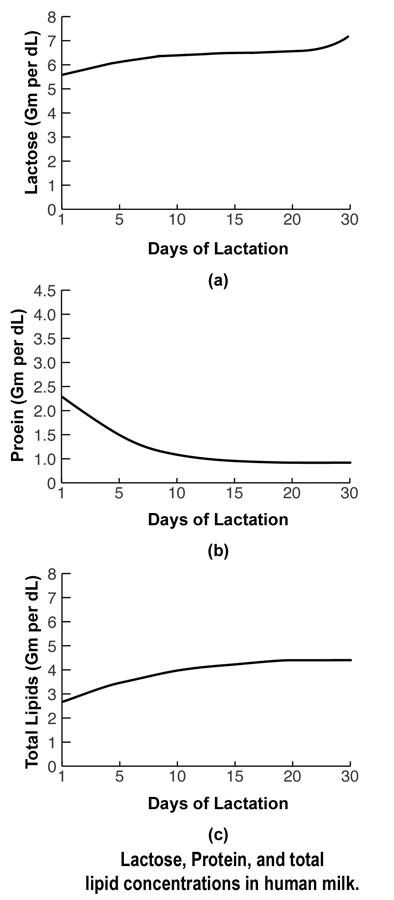
The pathways for milk secretion and synthesis by the mammary epithelial cell. I: Exocytosis of milk protein, lactose, and other components of the aqueous phase in Golgi-derived secretory vesicles. II: Milk fat secretion via the milk fat globule. III: Direct movement of monovalent ions, water, and glucose across the apical membrane of the cell. IV: Transcytosis of components of the interstitial space. V: The paracellular pathway for plasma components and leukocytes. Pathway V is open only during pregnancy, involution, and in inflammatory states such as mastitis. SV = Secretory vesicle; RER = Rough endoplasmic reticulum; BM = Basement membrane; MFG = Milk fat globule; CLD = Cytoplasmic lipid droplet; N = Nucleus; PC = Plasma cell; FDA = Fat-depleted adipocyte; TJ = Tight junction; GJ = Gap junction; D = Desmosome; ME = Myoepithelial cell. The processing and packaging of nutrients within human milk changes over time as the recipient infant matures. For example, early milk or colostrum has lower concentrations of fat than mature milk but higher concentrations of protein and minerals (see the image below). This relationship reverses as the infant matures.
Lactose, protein, and total lipid concentrations in human milk. Important biochemical points are discussed below. Fore and hind milk (important differences) In addition to the changes from colostrum to mature milk that mirror the needs of the developing neonate, variation exists within a given breastfeeding session. The milk first ingested by the infant (fore milk) has a lower fat content. As the infant continues to breastfeed over the next several minutes, the fat content increases. This hind milk is thought to facilitate satiety in the infant. Finally, the diurnal variations in breast milk reflect maternal diet and daily hormonal fluctuations. Specific enzymes to aid neonatal digestion Human milk contains various enzymes; some are specific for the biosynthesis of milk in the mammary gland (eg, lactose synthetase, fatty acid synthetase, thioesterase), whereas others are specific for the digestion of proteins, fats, and carbohydrates that facilitate the infant's ability to break down food and to absorb human milk. Certain enzymes also serve as transport moieties for other substances, such as zinc, selenium, and magnesium. Three-dimensional structure of human milk Under a microscope, the appearance of human milk is truly amazing. Although it is a fluid, human milk has substantial structure in the form of compartmentation. Nutrients and bioactive substances are sequestered within the various compartments of human milk. The most elegant example of this structure involves lipids. Lipids are enveloped at the time of secretion from the apical mammary epithelial cell within its plasma membrane, becoming the milk-fat globule. Certain proteins, growth factors, and vitamins also become sequestered within this milk-fat globule and are embedded within the membrane itself. The membrane acts as a stabilizing interface between the aqueous milk components and compartmentalized fat. This interface allows controlled release of the lipolysis products and transfer of polar materials into milk serum (aqueous phase). The bipolar characteristics of the membrane are also necessary for the emulsion stability of the globules themselves; thus, the structure of human milk provides readily available fatty acids and cholesterol for micellar absorption in the small intestine. Proteins, carbohydrates, and designer fats for optimal brain development Human milk provides appropriate amounts of proteins (primarily alpha-lactalbumin and whey), carbohydrates (lactose), minerals, vitamins, and fats for the growing term infant. The fats are composed of cholesterol, triglycerides, short-chain fatty acids, and long-chain polyunsaturated (LCP) fatty acids. The LCP fatty acids (18- to 22-carbon length) are needed for brain and retinal development. Large amounts of omega-6 and omega-3 LCP fatty acids, predominately the 20-carbon arachidonic acid (AA) and the 22-carbon docosahexaenoic acids (DHAs), are deposited in the developing brain and retina during prenatal and early postnatal growth. An infant, particularly a preterm infant, may have a limited ability to synthesize optimal levels of AA and DHA from linoleic and linolenic acid. Therefore, these 2 fatty acids may be considered essential fatty acids. Many infant formulas in the United States have added AA, DHA, or both. The amount of AA and DHA in breast milk varies with the maternal diet.[1, 9] The unique blend of fatty acids in the breast milk has been linked to the development of innate and adaptive immune regulation. Prior to routine fortification of formulas with DHA and AA, infants who received breast milk demonstrated better visual acuity at age 4 months than formula-fed infants, as well as slightly enhanced cognitive development. This has not been a universal finding, however, and some have continued to doubt the benefits of DHA and ARA. However, in a study of children at age 5 years who were breastfed and whose mothers were given a modest DHA supplement until 4 months postpartum, there was a significant improvement in sustained attention when compared to children whose mothers were not given DHA.[10] A study compared growth and bone mineralization in very low birth weight infants fed preterm formula with those who received term formula; the conclusion was that preterm formula better aided in growth and development.[11] One study examined maternal dietary manipulation of fatty acid concentration and neurodevelopmental differences in human milk.[12] Despite higher levels of AA and DHA in the heavily supplemented maternal groups, no differences were observed in the neurodevelopmental outcomes of the 3 groups. This finding supports a more global effect of human milk as opposed to a single agent that renders developmental differences. Thus, whether healthy term infants benefit from the addition of DHA and AA to formula remains unclear because they are able to convert very LCP fatty acids to DHA and AA. Ill term infants and those born prematurely are most likely to benefit from formulas enriched with DHA, AA, or both. Rather than producing better vision or greater intelligence, breast milk may somehow protect the developing neonatal brain from injury or less optimal development by providing necessary building materials and growth factors that act synergistically rather than in isolation. A study by Dallas et al indicated that milk produced by women who deliver preterm demonstrates a high level of protein breakdown by endogenous proteases, with the investigators suggesting that such breakdown may reduce difficulties associated with the immature digestive systems of preterm infants. The study, which looked at a total of 32 term and 28 preterm milk samples (from eight mothers and 14 mothers, respectively), found preterm milk to have a significantly higher peptide count than term milk. Cleavage-site analysis suggested that the protease plasmin is more active in preterm milk and that cytosol aminopeptidase and carboxypeptidase B2 also break down milk proteins.[13] Immunologic properties of human milkThrough the years, knowledge about the immune properties and effects of human milk has grown. A recommended comprehensive review by one of the pioneers in the field, Dr. Armand Goldman, appeared in Breastfeeding Medicine (2007).[14] Below are the highlights of just some of many known immune properties and functions of human milk.
Bioactive properties of human milkHuman milk also contains growth modulators, such as epidermal growth factor (EGF), nerve growth factor (NGF), insulinlike growth factors (IGFs), and interleukins. Transforming growth factor (TGF)–alpha, TGF-beta, and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) are also identified in human milk. These growth modulators are produced either by the epithelial cells of the mammary gland or by activated macrophages, lymphocytes (mainly T cells), or neutrophils in the milk. EGF and TGF-alpha were found at higher concentrations in the milk of mothers who delivered prematurely compared with those who delivered at term. EGF, TGF-alpha, and human milk stimulate fetal small intestinal cell proliferation in vitro, with the greatest increase in cell proliferation seen following exposure to human milk. Certain bioactive substances and live cells in milk appear to influence neonatal gut maturation and growth through their transfer of developmental information to the newborn. Although most of these biosubstances have been identified in mother's milk in quantities that exceed maternal serum levels, their exact role in human newborns is uncertain; most current information is from animal models whose development may significantly differ. ConclusionHuman milk, in addition to its numerous nutrients that make it an ideal food source for the growing term infant, is a bioactive fluid that evolves from colostrum to mature milk as the infant matures. This bioactive fluid contains numerous factors and live cells that, in concert, promote the growth and well-being of the breastfeeding infant. Oliver Wendell Holmes said it best when he stated, "A pair of substantial mammary glands has the advantage over the two hemispheres of the most learned professor's brain, in the art of compounding a nutritious fluid for infants." With the ever-expanding knowledge resulting from current research, commercial formula clearly cannot replicate all of the valuable properties that are inherent in human milk. Main Reference: http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1835675-overview#showall |